Introduction to Cyber Security Threats

Cyber security threats are a growing concern in our increasingly connected world. As the number of connected devices and networks rapidly increase, so too do the opportunities for malicious actors to exploit vulnerable systems. Cyber security threats can come in many forms, including malicious software, or malware; unauthorized access to systems and data; and data manipulation or theft. All of these types of threats can cause significant harm, from financial losses to reputational damage. In order to protect against these threats, organizations must have an effective and up-to-date security strategy in place. This strategy should include measures such as user and device authentication, data encryption, patching of systems and applications, and regular security assessments.
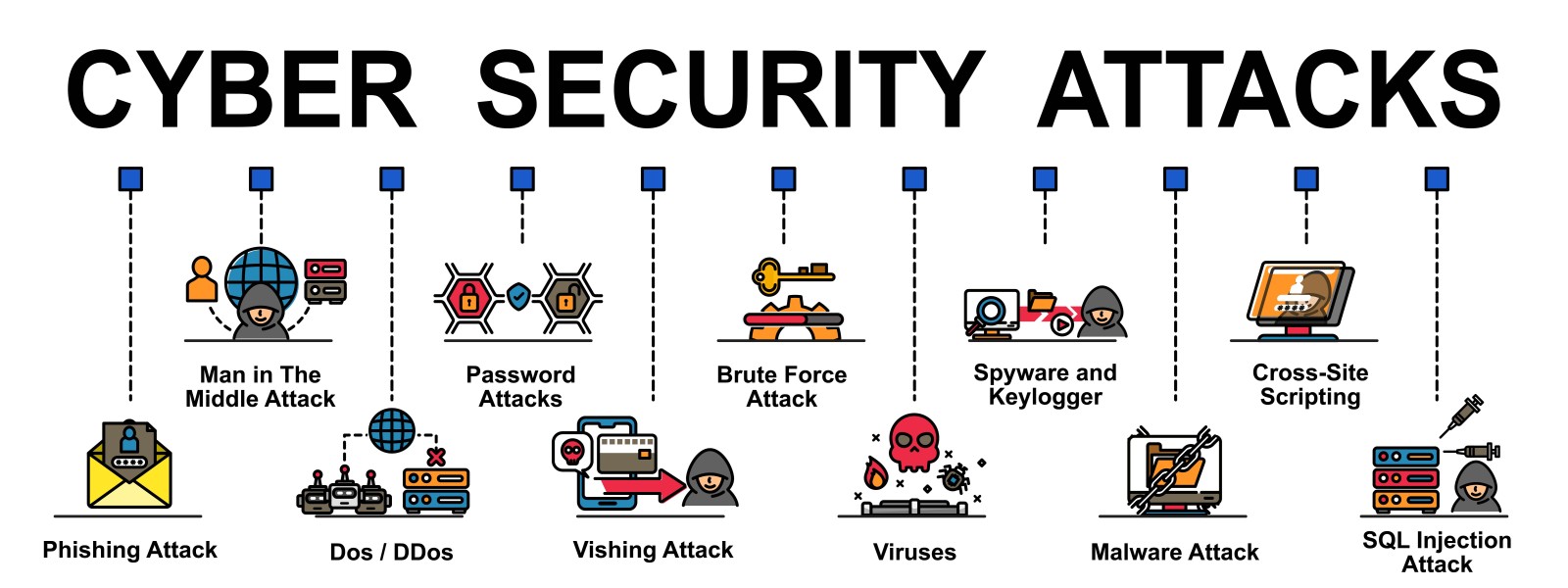
What are the Most Common Cyber Security Threats

Cyber security threats are a ubiquitous and ever-growing concern in the modern world. Malicious actors are constantly evolving their tactics in order to circumvent standard cyber security measures and gain access to sensitive data. The most common cyber security threats include malware, phishing, social engineering, denial of service attacks, and data breaches. Malware is a form of malicious software, typically installed on a victim’s computer without their knowledge or consent. Phishing is the practice of sending deceptive emails designed to trick users into revealing sensitive information or click on malicious links. Social engineering is the process of manipulating unsuspecting users into revealing confidential information or allowing malicious actors access to restricted systems.
Malware
Malware, a portmanteau of malicious software, refers to any computer program or code that is designed to disrupt, damage, or take unauthorized control of a computer or system. It is a broad term that encompasses all sorts of malicious code and software, including viruses, worms, Trojans, spyware, adware, ransomware, and other malicious software. Malware is often used to gain access to confidential information or to spread malicious content to other computers or networks. It can also be used to disrupt the normal operation of a computer or system, making it difficult or impossible to function correctly. Malware can be spread through various means, such as email attachments, downloads, instant messages, removable media, and even through malicious websites.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that is designed to deny access to data until a ransom is paid. It works by encrypting data on a device, making it inaccessible unless the victim pays a fee or meets some other demand. The ransom typically must be paid in a cryptocurrency such as Bitcoin, as this provides a degree of anonymity to the attacker. Once the ransom is paid, the attacker will usually send a decryption key that can be used to restore access to the data. Ransomware has become increasingly common in recent years, and it is estimated that hundreds of millions of dollars were paid in ransom to attackers in 2020. Ransomware attacks can have serious financial and reputational consequences for victims.
Fileless Attacks
Fileless attacks refer to malicious activities that can be executed without the need for a malicious file to be downloaded or stored on a computer. These attacks are becoming increasingly popular for malicious actors as they are more difficult to detect and can bypass most traditional security solutions such as anti-virus and intrusion detection systems. Fileless attacks typically involve leveraging legitimate tools or administrative privileges that are already present on the system to execute malicious code. Examples of these attack vectors include PowerShell, WMI, and registry modification, among others. Furthermore, attackers can use memory-only malware, which is stored in the system’s memory rather than on disk, to carry out malicious activities and evade detection. To successfully mitigate fileless attacks, organizations need to adopt a layered security approach.
DoS and DDoS Attacks
DoS (denial-of-service) and DDoS (distributed denial-of-service) attacks are malicious activities used to disrupt the availability of online services. Utilizing a variety of techniques, a DoS attacker attempts to overwhelm a system’s resources, making it unable to respond to legitimate requests. A DDoS attack, on the other hand, takes advantage of multiple compromised systems, which are used to target a single system. The larger the number of systems involved, the more difficult it is to counteract the attack. Common methods used in DoS and DDoS attacks include flooding the target with requests, overwhelming the system with illegitimate traffic, or using malicious code that can cause the target system to crash.
Phishing
Phishing is a technique used by cyber criminals to deceive victims into providing sensitive information by disguising as a trustworthy source. It is a form of social engineering which involves creating malicious emails and websites that appear to be legitimate, in order to persuade victims to divulge confidential data. Typically, attackers will target a large group of users through a mass email campaign, hoping to trick at least a few of them into clicking on a malicious link or downloading a malicious attachment. Once a user has been tricked into providing their credentials, the attacker can use them to gain access to the user’s device or network. It is important for users to remain vigilant when it comes to phishing attempts, as attackers are constantly changing their tactics and becoming more sophisticated.
Account Takeover
Account takeover is a type of cyber-attack wherein a malicious actor gains unauthorized access to an online account belonging to another individual or entity. This type of attack is particularly dangerous as it can lead to the theft of sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and payment details, as well as the potential to commit fraud or other malicious activities. Account takeover attacks can occur in a variety of ways, such as social engineering, phishing, and malware, and the effects can be devastating, both in terms of financial costs and damage to a company’s reputation. To guard against account takeover, organizations must ensure their systems are secure and regularly monitor for suspicious activity. Additionally, users should maintain strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication when available.
MitM Attacks
MitM attacks are a type of cyberattack that generally targets accounts on various networks and systems. This type of attack is commonly used by malicious actors to gain access to an account on a particular system or network, with the intention of using the account for nefarious activities. The attacks typically involve the attacker obtaining the credentials of the account (e.g. username and password) through a variety of methods such as phishing, social engineering, or other malicious techniques. Once the credentials are obtained, the attacker can then log into the account and gain access to the targeted system or network. MitM attacks are highly dangerous and can be used to perform a variety of malicious activities including privilege escalation, data exfiltration, and account takeover.
Summing up

In conclusion, it can be said that the most common cyber security threats are the result of malicious actors attempting to gain unauthorized access to data or systems. These threats usually manifest as viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, phishing attacks, and other malicious software. The methods by which malicious actors attempt to gain access are constantly evolving, as is the technology used to detect and prevent them. Nonetheless, the most effective way to combat these threats is to ensure user and system security through the implementation of best practice security controls, such as strong passwords, two-factor authentication, patching and vulnerability management, and regular monitoring of user and system activity.